< Home Page
Earth Magnetic Field
The invisible energy that extends from the Earth interior
The source of Earth magnetic field (geomagnetic field) is still a mystery but it is believed to be generated by the liquid iron interior of Earth.
Earth magnetic field is so important that without it, our world will be completely different. The magnetic field is not only important for navigation, it also act as an energy shield to protect live on Earth from space radiation.
Most radiation come from the Sun, and the Earth's magnetic field divert most of the charged particles from reaching Earth's atmosphere.
The magnetosphere is the planet's first line of defense against the solar wind and cosmic radiation.
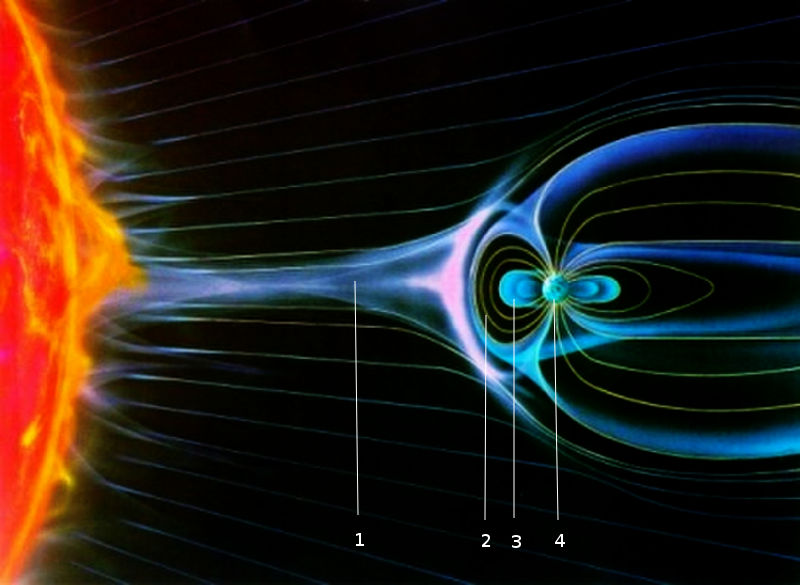
Image source: NASA
1. Solar wind charged particle
2. Magnetic field line
3. Van Allen belt
4. Earth
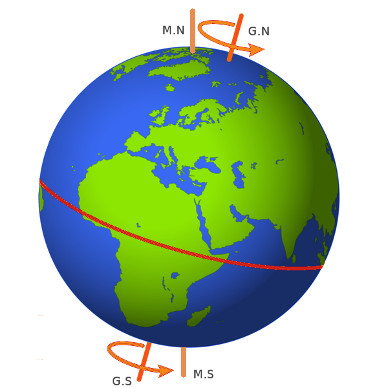
What is "True North" and "Magnetic North"?
True North is the north pole
True north is the direction in which the north pole is located along the earth's rotational axis. It is also called the geographical north.
Magnetic North is the compass north
The magnetic north deviates from true north and the exact location changes from time to time
Geomagnetic reversal
When the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south interchanged, it's called "Geomagnetic reversal". It is reported that there have been 183 reversals over the last 83 million years.
Reference Source:
https://en.wikipedia.org/
Magnetic declination
Magnetic declination is the angle between compass north (magnetic north) and true north( geographical north ).
- When magnetic north is east of true north, it's called positive declination
- When magnetic north is west of true north, it's called negative declination
| Location |
Declination Value |
| Boston |
~ -15° |
| Hong Kong |
~ -2° |
| London |
~ -1° |
| Moscow |
~ +10° |
| New Delhi |
~ +1° |
| Shanghai |
~ -5° |
| Seoul |
~ -8° |
| Sydney |
~ +12° |
| TaiPei |
~ -3° |
| Tokyo |
~ -7° |
| Vladicostok |
~ -10° |
We could manually adjust a magnetic compass to get the true north direction.
There is one of the online resources for getting the updated declination.
http://magnetic-declination.com/
Reference Source:
http://en.wikipedia.org/
Alternatively, we could use a GPS APP to get the "real" direction.
However, a GPS system can only tell us the direction of movement.
If we stay stationary, it can not tell the direction. This is the main limitation of using GPS.
Free GPS Tool for download
GPS Tool - Speed Distance Altitude
Type of magnetic field and public health
International organizations, for example WHO and ICNIRP have been active in the evaluation of health issues raised by exposure to electromagnetic fields (EMF). Generally speaking, the magnetic field we exposed in daily life is relatively low and do not have negative health effect. However, some people are more sensitive and protection measures should be taken if necessary. Magnetic fields can be classified in 3 categories.
- Static magnetic field (0 Hz)
- LF magnetic field (1-100 kHz)
- HF magnetic field (100 kHz - 300 GHz)
Static magnetic field
Static magnetic fields are constant fields, which do not change in intensity or direction over time. Earth magnetic field is static magnetic field. The natural magnetic field varies over places between about 30 to 70 µT and is perceived by certain animals that use it for orientation. Static magnetic field can be generated by a magnet or single direction electric current.
LF magnetic field
LF magnetic fields are mainly related to electric power generation, distribution and use in AC equipment. The frequency used for this purpose is usually 50 or 60 Hz depending on country. In daily life, people are exposed to LF fields around electric appliances and electronic devices mostly at home and at work. Power lines are also a source of LF fields. Background magnetic fields at home are usually less than 0.1 µT
HF magnetic field
HF magnetic fields are mainly related to communication equipment (e.g. mobile phones, base stations, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, radio, TV, security devices), medical equipment, navigation system, military radar, and also for heating purposes (e.g. microwave ovens).
Public exposure reference
| Static magnetic field |
Reference Value |
| General public exposures |
40 mT (ICNIRP 1994) / 400 mT (ICNIRP 2009) |
| People with implanted electronic medical device |
0.5 mT(500 µT) |
| LF / HF magnetic field |
Reference Value |
| 1 Hz |
40000 µT |
| 8 Hz |
625 µT |
| 50 Hz |
0.1 µT |
| 0.8 kHz - 150 kHz |
6.25 µT |
| 10 MHz - 400 MHz |
0.092 µT |
| 400 MHz - 2000 MHz |
0.0046 x ƒ 0.5 µT
(900 MHz -> 0.138 µT)
(1800 MHz -> 0.195 µT) |
| 2 GHz - 300 GHz |
0.2 µT |
* Reference:
ICNIRP - Limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic and electromagnetic fields
Other Reference:
WHO - What is EMF
WHO - EMF and public health (Static magnetic field)
WHO - EMF and public health (LF magnetic field)
WHO - EMF and public health (Radar)
WHO - EMF and public health (Base Station)
WHO - Environmental Health Criteria Monograph No.238 - Extremely Low Frequency Fields
ICNIRP - Static Magnetic Fields
ICNIRP - LF Magnetic Fields
ICNIRP - HF Magnetic Fields
Magnetic Strength Reference Values
* 25 - 70 µT – strength of magnetic field on Earth's surface
* 31.869 µT – strength of Earth's magnetic field at 0° latitude, 0° longitude
* 5 mT – the strength of a typical refrigerator magnet
* 0.3 T – the strength of solar sunspots
* 1 T to 2.4 T – coil gap of a typical loudspeaker magnet
* 13 T – strength of ITER fusion reactor
Source:
http://en.wikipedia.org/

